Database migration testing
The DBLab Engine's ability to instantly create full-size clones of your production database allows you to integrate fully automated DB migration testing into your CI/CD pipeline. Learn how the DBLab Engine works.
Realistic DB migration testing is hard
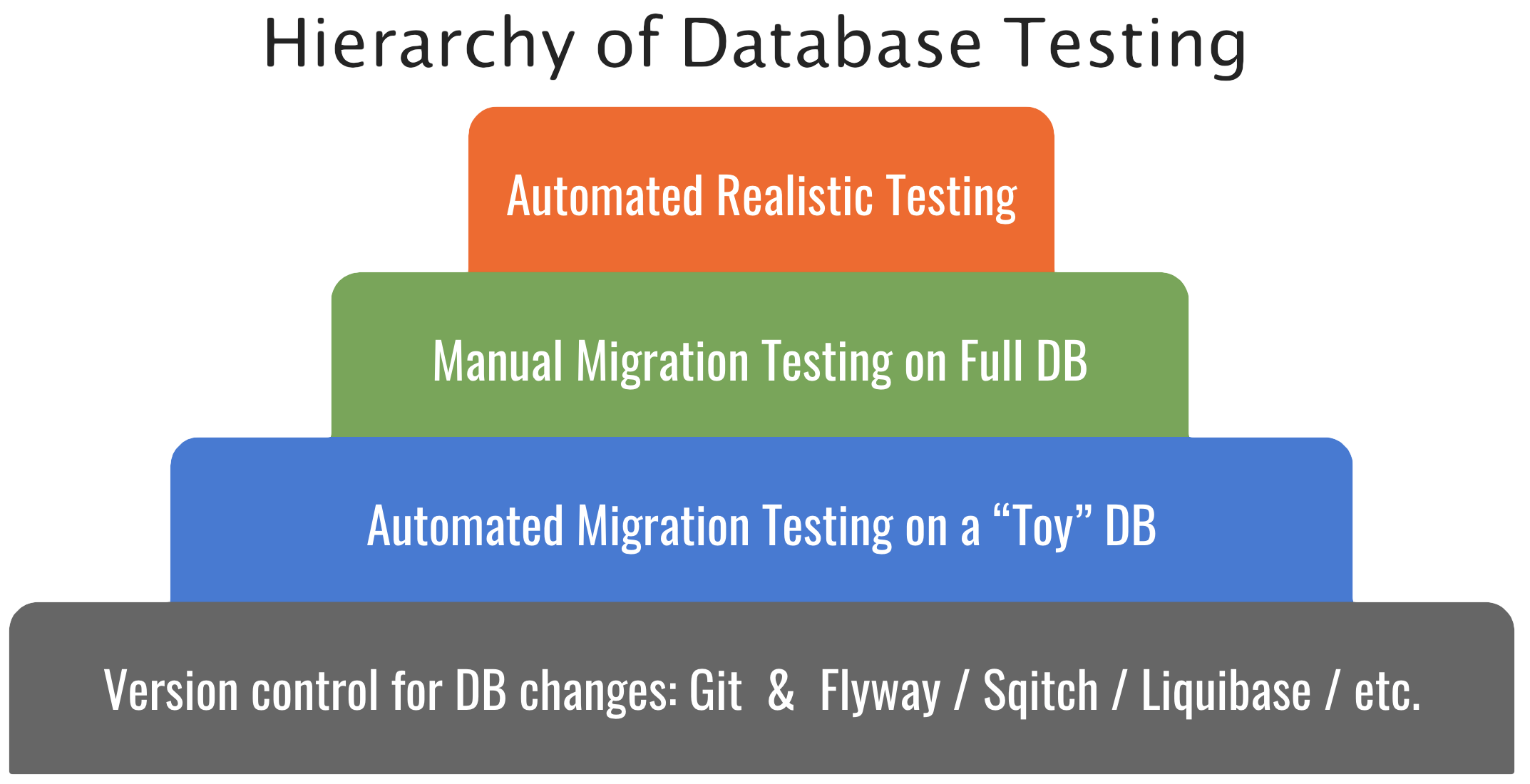
Nearly every software organization invests in a full suite of automated tests that validate an application's runtime behavior. However, very few are able to automatically validate an application's deploy-time behavior.
For most organizations, automated DB migration testing is simply too time-intensive and costly. Using conventional methods, provisioning a full-size copy of the database could take hours (or days!) and significantly increase compute and storage costs.
No testing means unexpected problems
However, the absence of realistic migration testing presents significant risks including failed deploys and unexpected application downtime.
Here are just a few of the most common problems when migrations aren't tested in a realistic environment:
- A lock is held for an extended time period causing a cascade of failures
- A query hits a
statement_timeoutand aborts the DB migration (or leaves the application in a partially migrated state) - The database contains unanticipated values causing unexpected behavior or even data loss
Database Lab makes realistic testing easy
The DBLab Engine eliminates the time and cost that make it difficult to set up automated testing of database migrations. Companies can use the DBLab Engine to build a migration specific CI job which:
- Instantly creates a thin clone of the production database
- Executes pending migrations against the clone
- Reports status, statistics, and valuable metadata
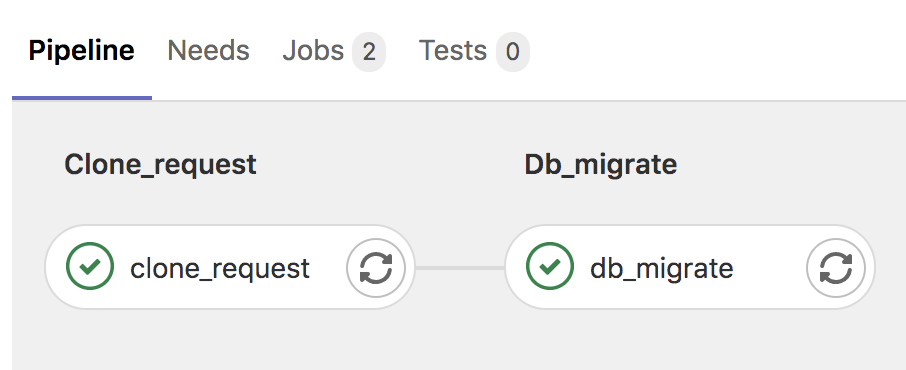
Companies that use Database Lab to test their DB migrations will gain full visibility into their applications' deploy-time behavior eliminating a major source of risk.
Explore our examples to see how this works in practice using GitHub Actions.