13. Lock contention analysis
Monitor lock waits and identify blocking chains.
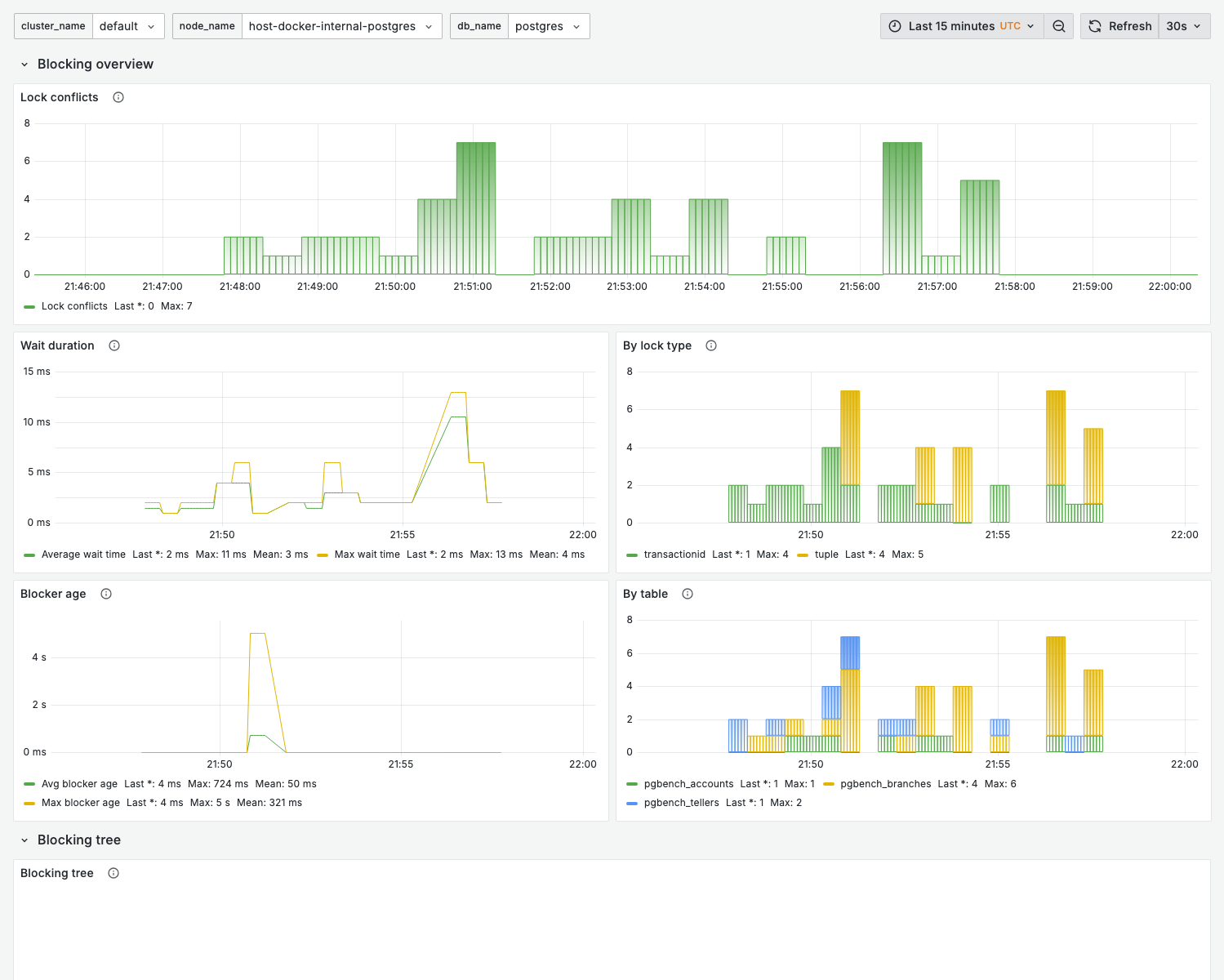
Screenshot note
This dashboard only shows data when lock contention is occurring. In low-contention environments, panels will be empty. This is expected behavior — an empty dashboard indicates healthy lock performance.
Purpose
Diagnose lock-related performance issues:
- Identify blocking queries
- Find lock contention hotspots
- Analyze deadlock patterns
- Plan maintenance windows
When to use
- Applications experiencing lock timeout errors
- Queries waiting unexpectedly
- During DDL operations
- Investigating deadlocks
Key panels
Lock waits over time
What it shows:
- Number of sessions waiting for locks
- Lock wait duration distribution
Warning signs:
- Sustained lock waits
- Increasing wait times
- Correlation with specific operations
Blocking chains
What it shows:
- Which sessions are blocking others
- Depth of blocking chains
Interpretation:
- Single blocker affecting many — address that query
- Deep chains — potential design issue
Locks by type
What it shows:
- Distribution of lock types
- Most common contention points
| Lock type | Description | Common cause |
|---|---|---|
RowExclusiveLock | Row modifications | UPDATE/DELETE conflicts |
AccessShareLock | SELECT operations | Long-running queries |
AccessExclusiveLock | DDL operations | ALTER TABLE, DROP |
ShareLock | Index creation | CREATE INDEX |
Lock wait duration
What it shows:
- How long queries wait for locks
- Percentile distribution
Variables
| Variable | Purpose |
|---|---|
cluster_name | Cluster filter |
node_name | Node filter |
db_name | Database filter |
Lock analysis queries
Current lock waits
select
blocked.pid as blocked_pid,
blocked.query as blocked_query,
blocking.pid as blocking_pid,
blocking.query as blocking_query,
now() - blocked.query_start as wait_duration
from pg_stat_activity as blocked
join pg_locks as blocked_locks
on blocked.pid = blocked_locks.pid
join pg_locks as blocking_locks
on blocked_locks.locktype = blocking_locks.locktype
and blocked_locks.database is not distinct from blocking_locks.database
and blocked_locks.relation is not distinct from blocking_locks.relation
and blocked_locks.page is not distinct from blocking_locks.page
and blocked_locks.tuple is not distinct from blocking_locks.tuple
and blocked_locks.virtualxid is not distinct from blocking_locks.virtualxid
and blocked_locks.transactionid is not distinct from blocking_locks.transactionid
and blocked_locks.classid is not distinct from blocking_locks.classid
and blocked_locks.objid is not distinct from blocking_locks.objid
and blocked_locks.objsubid is not distinct from blocking_locks.objsubid
and blocked_locks.pid != blocking_locks.pid
join pg_stat_activity as blocking
on blocking_locks.pid = blocking.pid
where not blocked_locks.granted
order by wait_duration desc;
Lock statistics by table
select
relname,
mode,
granted,
count(*)
from pg_locks l
join pg_class c on l.relation = c.oid
where relnamespace = 'public'::regnamespace
group by relname, mode, granted
order by count(*) desc;
Recent deadlocks
Check PostgreSQL logs for deadlock entries, or use:
select
datname,
deadlocks
from pg_stat_database
where deadlocks > 0;
Resolving lock issues
Immediate actions
-
Identify the blocker:
select pid, query, state, wait_event
from pg_stat_activity
where pid in (select pid from pg_locks where not granted); -
Terminate if necessary:
select pg_terminate_backend(blocking_pid);
Preventive measures
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Long transactions | Set idle_in_transaction_session_timeout |
| DDL during traffic | Use lock_timeout, schedule maintenance |
| Hot row contention | Review application design |
| Deadlocks | Consistent lock ordering in application |
Related dashboards
- Wait events — 04. Wait Events
- Query analysis — 02. Query Analysis
- Node overview — 01. Node Overview
Troubleshooting
No lock data shown
- Verify there are actual lock waits occurring
- Check time range — lock waits may be brief
Frequent deadlocks
- Review application transaction patterns
- Ensure consistent lock ordering
- Consider advisory locks for complex scenarios
- Check for missing indexes causing full table locks